The Science Behind Aluminum Cladding’s Fire Resistance Capabilities

5 Economic Advantages of Using Aluminum Cladding in Construction
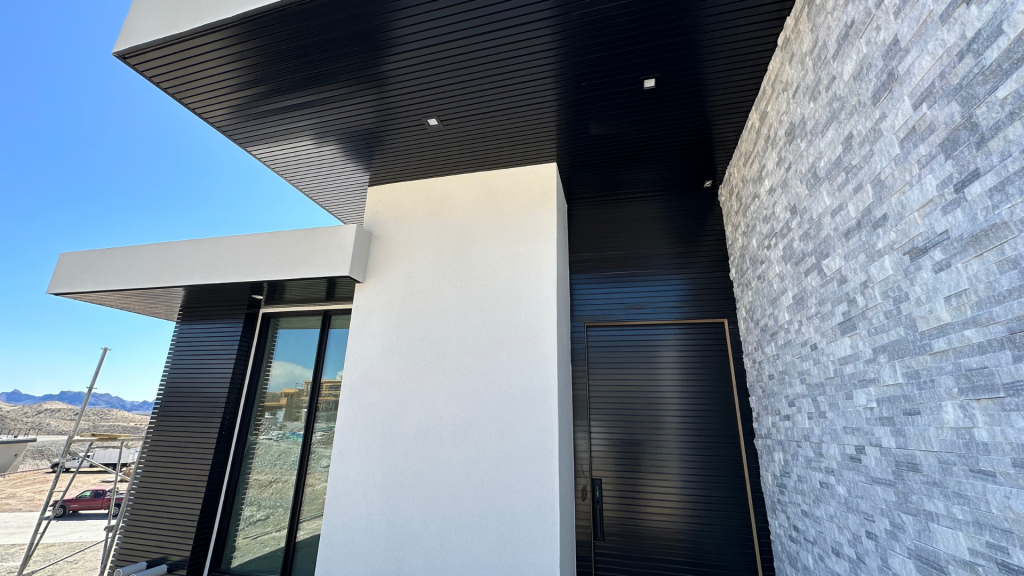

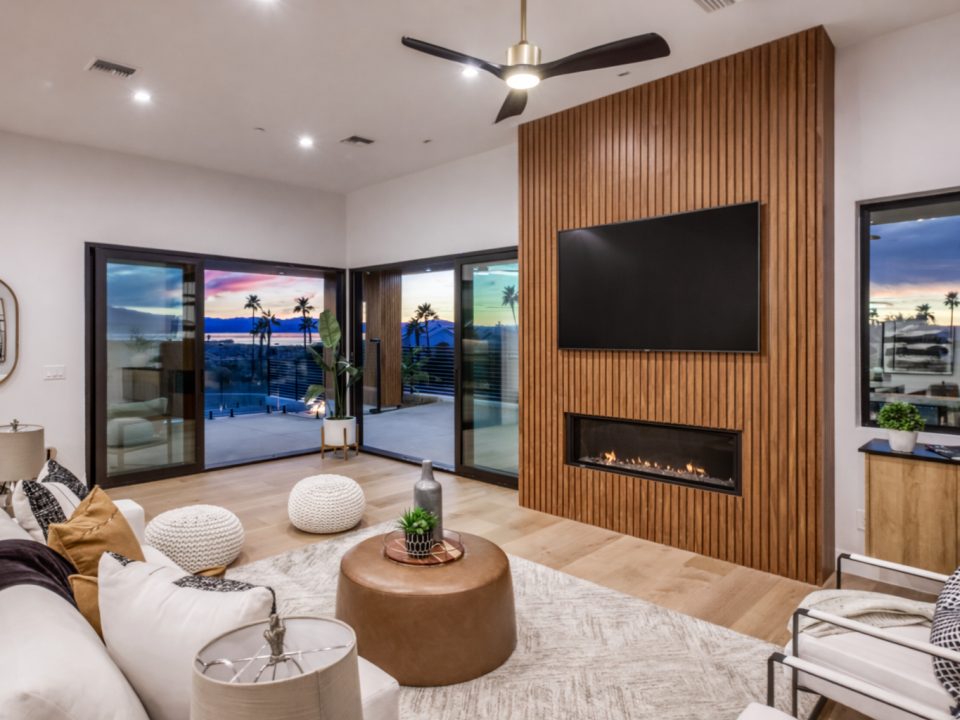
In modern construction, achieving optimal building safety and insulation is crucial, especially in regions subject to harsh climates. Aluminum cladding has emerged as a versatile and effective solution due to its lightweight yet resilient nature.
This blog aims to provide a comprehensive guide on how aluminum cladding can address unique challenges posed by extreme weather conditions, while enhancing the overall safety and energy efficiency of buildings.
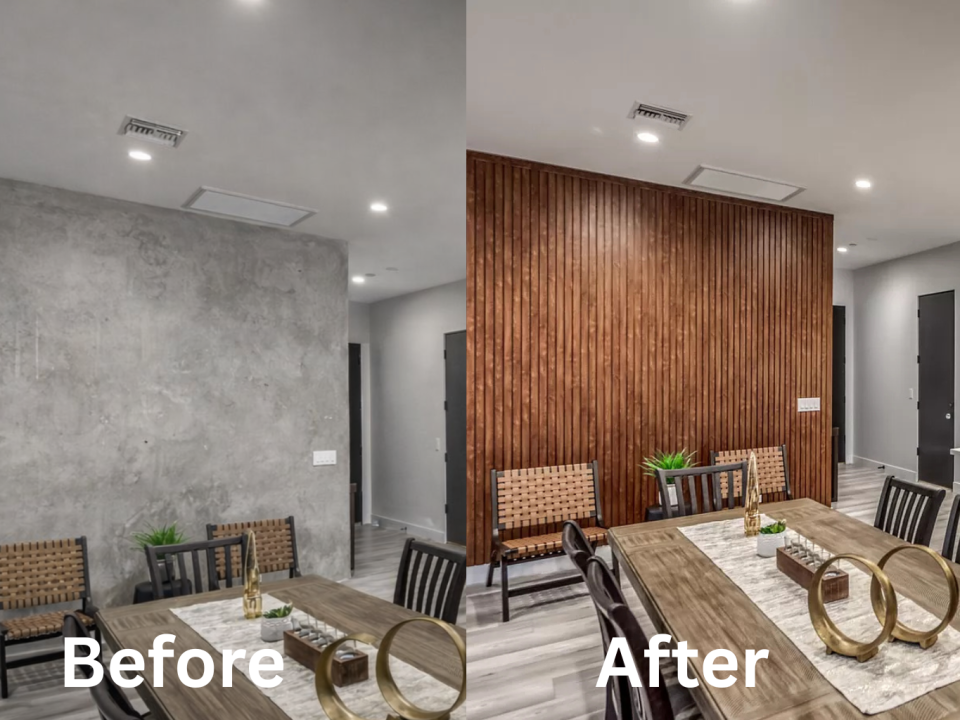
The unique properties of aluminum make it ideal for architectural facades and building exteriors. It’s durable, corrosion-resistant, and capable of being recycled repeatedly without losing quality.
Moreover, its ability to reflect heat and its structural strength contribute significantly to buildings remaining comfortable and protected even under the most challenging weather conditions.
However, optimizing these benefits requires a strategic approach. This blog explores eight fundamental best practices and materials for implementing aluminum cladding effectively in harsh climates.
By understanding how to choose the right alloy and finish, ensuring proper installation, and maintaining regular inspection routines, architects and builders can make the most of aluminum cladding’s potential to protect and enhance their projects.
Best Practice 1: Choose the Right Alloy and Finish
One of the primary considerations is selecting an appropriate aluminum alloy and finish. Not all aluminum is the same, and various alloys offer differing levels of resistance to corrosion and stress.
High-grade alloys like the 3000 or 5000 series are often recommended for cladding in harsh climates because they offer excellent corrosion resistance.
Anodized finishes or PVDF coatings can further protect the surface from UV rays, salt water, and acid rain, which are common in coastal or highly polluted areas. GTO Aluminum, for instance, offers coated finishes that adhere to these high standards, providing additional longevity.
Best Practice 2: Proper Installation Techniques
Correct installation techniques are crucial in harsh climates to prevent moisture intrusion, thermal bridging, and structural weaknesses. Employing weather-resistant barriers behind the cladding, ensuring tight seals, and allowing room for thermal expansion can significantly improve the system’s performance.
GTO Aluminum’s Universal Click-Profile System, for instance, allows for rapid and secure installation while also accommodating building movements and thermal expansion. This helps in maintaining the integrity of the cladding over time and prevents water infiltration.
Best Practice 3: Routine Maintenance and Inspection
Even with the most resilient materials, regular inspection and maintenance are essential to maximizing the lifespan of aluminum cladding. In harsh climates, this includes checking for signs of corrosion, panel warping, and seal deterioration.
A routine cleaning schedule should also be implemented to remove any salt buildup, acid rain residues, or pollution that could accelerate surface degradation. By catching potential issues early, these maintenance practices can extend the life of the cladding system.
Best Practice 4: Incorporate Thermal Insulation Layers
In extreme climates, temperature regulation is key. Incorporating a thermal insulation layer behind the aluminum cladding ensures that buildings remain comfortable while reducing energy costs. This insulation layer can prevent excessive heat gain or loss and, when paired with aluminum’s reflective properties, enhances overall energy efficiency. This results in a more comfortable interior environment and a significant reduction in heating or cooling expenses.
Best Practice 5: Opt for Impact-Resistant Systems
Harsh climates often involve high winds, hail, or flying debris. Opting for aluminum cladding systems that are impact-resistant can help mitigate damage in storm-prone areas. Reinforced aluminum panels or systems with interlocking seams prevent dislodging or denting from harsh weather conditions, reducing the need for expensive repairs and minimizing long-term maintenance costs.
Best Practice 6: Utilize Ventilated Rainscreen Systems
A ventilated rainscreen system provides an additional layer of defense by allowing water and moisture to drain or evaporate away from the building’s structural envelope. This system reduces condensation buildup and minimizes mould growth and corrosion risks. Proper ventilation ensures the cladding remains effective while extending the lifespan of the building’s facade.
Best Practice 7: Secure Seams and Fasteners Appropriately
Strong, durable fasteners and secure seam sealing ensure the cladding remains intact during high winds and extreme weather. Stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant fasteners and adhesives should be used to anchor the panels securely. Using appropriate fasteners minimizes the chance of the cladding loosening or detaching, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Best Practice 8: Apply Regular Weatherproof Coatings
Coating the aluminum surface with weatherproof finishes enhances corrosion resistance and protects against environmental degradation. High-quality coatings like fluoropolymer or powder coatings provide an added layer of defence against UV rays, moisture, and pollutants. Regular re-application of these coatings is crucial for maintaining the aluminum cladding’s durability and aesthetic appeal.
By adhering to these best practices, architects and builders can ensure their aluminum cladding systems deliver maximum performance and longevity, even in the harshest of climates.
In conclusion, aluminum cladding remains a powerful solution for buildings in harsh climates due to its combination of durability, insulation properties, and safety features.
The key to maximizing these benefits lies in selecting the right alloy and finish, ensuring proper installation techniques, and regularly inspecting and maintaining the panels.
Incorporating thermal insulation, opting for impact-resistant systems, and securing seams and fasteners appropriately all contribute to the longevity and resilience of the cladding.
Beyond these structural considerations, ventilated rainscreen systems and regular weatherproof coatings add further layers of defense, protecting buildings from temperature extremes, moisture buildup, and corrosive elements.
By adopting these practices, architects and builders can ensure that aluminum cladding systems provide reliable protection and contribute to the overall sustainability and efficiency of the building.
GTO Aluminum stands out as a key influencer in this field, ready to shape the future of aluminum cladding.