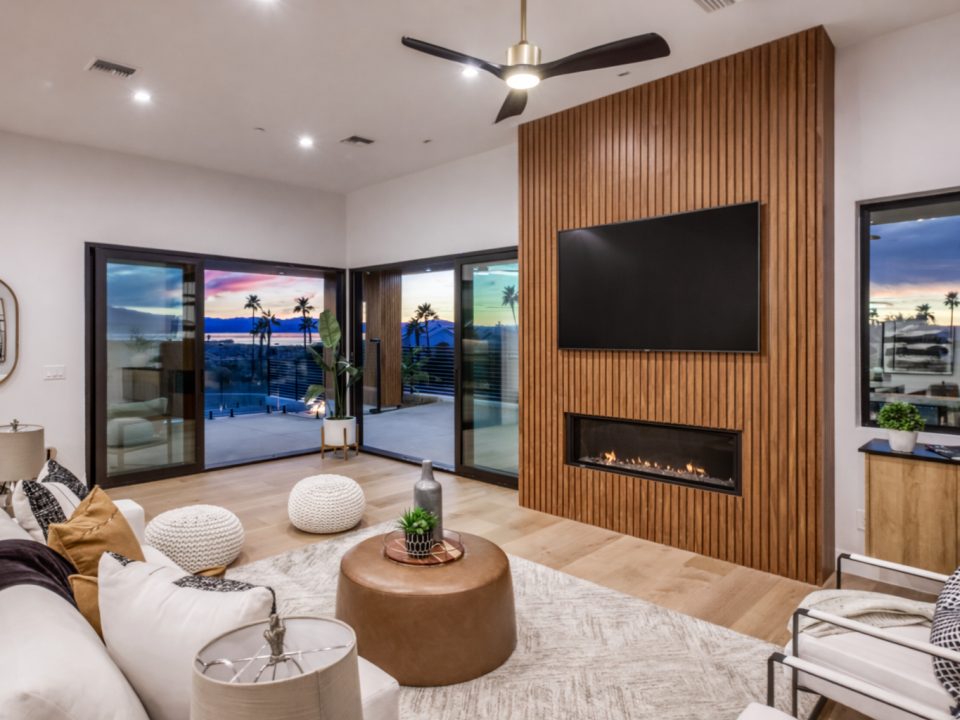
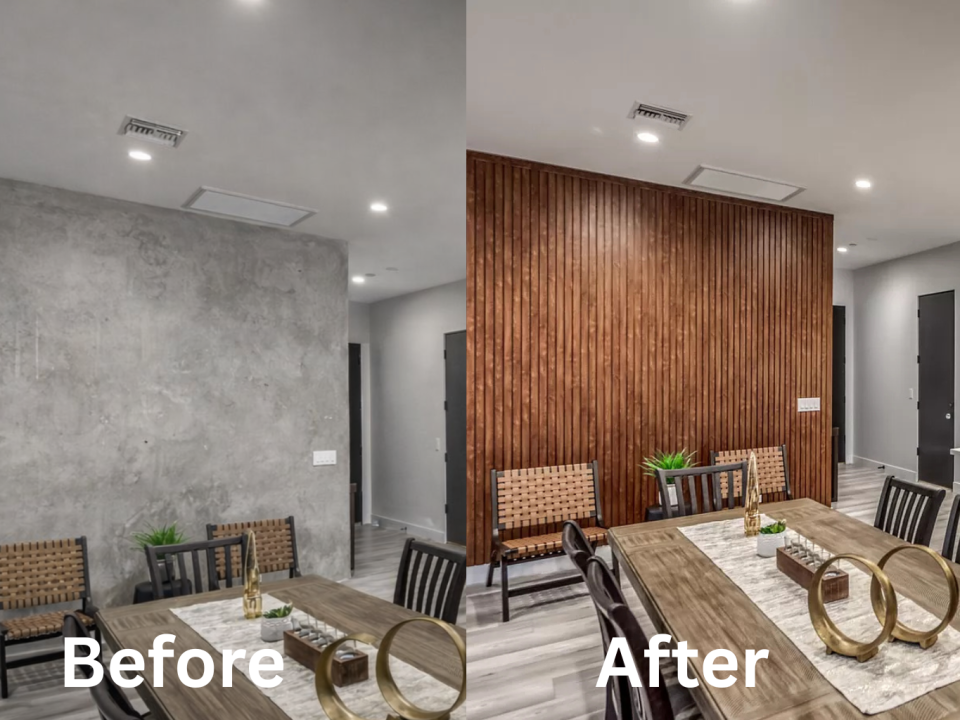
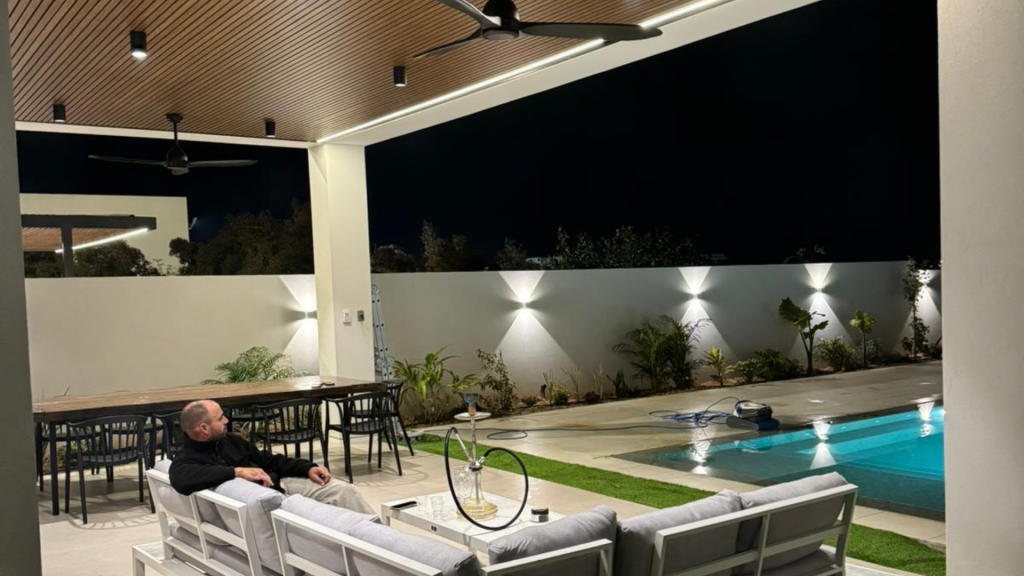
Why Architects Are Choosing Aluminum Cladding for Biophilic Design

From Traditional to Trendsetting: How Aluminum is Transforming Classic Architecture

Indoor air quality (IAQ) has become a critical consideration in modern architecture, impacting the health and comfort of building occupants. Poor air quality can lead to respiratory issues, allergies, and reduced productivity, which is why architects and builders are prioritizing materials and designs that promote a healthier indoor environment.
One of the emerging materials that offers both aesthetic and functional benefits is aluminum cladding. In addition to its durability and design flexibility, aluminum cladding can contribute significantly to improving IAQ.
Here’s how aluminum cladding plays a crucial role in enhancing indoor air quality in modern buildings.
1. Non-Toxic and Safe for Occupants
Aluminum cladding does not emit harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are often found in traditional building materials such as paints, adhesives, and sealants. VOCs are known to pollute indoor air, contributing to respiratory problems and long-term health issues.
Since aluminum is non-toxic, using it in cladding ensures that the air inside remains free from these pollutants. Additionally, aluminum’s resistance to mold and mildew growth further helps prevent the spread of airborne allergens that can compromise indoor air quality.
2. Ventilated Cladding Systems for Better Air Circulation
Modern aluminum cladding systems, particularly ventilated facades, allow for better air circulation within the building structure. A ventilated facade creates an air gap between the cladding and the building’s exterior, which helps in maintaining airflow and reducing the risk of moisture buildup.
By keeping moisture out, these systems prevent mold and mildew growth, which are common contributors to poor indoor air quality. Moreover, the natural ventilation provided by these facades helps in regulating temperature, reducing the need for artificial cooling and heating, which often recirculate indoor air.
3. Improved Moisture Management
One of the significant ways aluminum cladding improves IAQ is by managing moisture more effectively. Moisture inside a building can lead to condensation, dampness, and mold growth—all of which can degrade air quality. Aluminum cladding systems, especially when used in conjunction with proper insulation, act as a barrier to moisture.
They prevent water from infiltrating the structure and reduce humidity levels indoors. This moisture control is essential for maintaining a dry, mold-free indoor environment that promotes better air quality.
4. Reduced Need for Chemical Treatments
Unlike materials such as wood, aluminum cladding does not require regular chemical treatments, varnishes, or paints to maintain its appearance and integrity. This translates to fewer chemicals being used during the building’s lifecycle, which in turn means fewer harmful substances being released into the air over time.
The absence of off-gassing materials significantly contributes to healthier indoor air, especially in spaces like offices, schools, and healthcare facilities where air quality is of paramount importance.
5. Fire-Resistant Properties
Aluminum is non-combustible, which means it does not contribute to the spread of fire. In the unfortunate event of a fire, many traditional building materials can release harmful smoke and toxic gases, compromising air quality and endangering occupants.
Aluminum cladding, however, does not emit dangerous fumes when exposed to fire, ensuring that indoor air remains as safe as possible in emergency situations.
6. Sustainability and Air Quality
Aluminum’s sustainability also plays a role in improving indoor air quality. Aluminum is 100% recyclable, reducing the need for the production of new materials, which in turn lowers the environmental and air quality impacts of manufacturing.
Additionally, its durability means that buildings using aluminum cladding require fewer repairs and replacements over time, resulting in fewer construction disruptions that can contribute to dust and particulate matter in the air.
7. Energy Efficiency and Reduced HVAC Load
Energy-efficient aluminum cladding systems reduce the need for HVAC systems to overwork, thereby cutting down on the recirculation of indoor air. When buildings are too reliant on heating or air conditioning, it can lead to stagnant air, which often carries dust, allergens, and other pollutants.
Aluminum cladding’s thermal insulation properties help in regulating the indoor temperature naturally, allowing for less mechanical ventilation and a healthier airflow in the building.
Conclusion
Aluminum cladding is not just a sleek, modern design solution but also a vital contributor to enhancing indoor air quality. From preventing moisture buildup to reducing harmful chemical emissions, its impact on building health is significant.
Architects and builders looking to prioritize the health and safety of building occupants can greatly benefit from incorporating aluminum cladding into their designs. Its combination of durability, sustainability, and IAQ benefits makes aluminum cladding a smart choice for the future of healthy building design.
For more on how GTO Aluminum’s solutions can improve your building’s indoor air quality, visit gtoaluminum.com or contact us today!